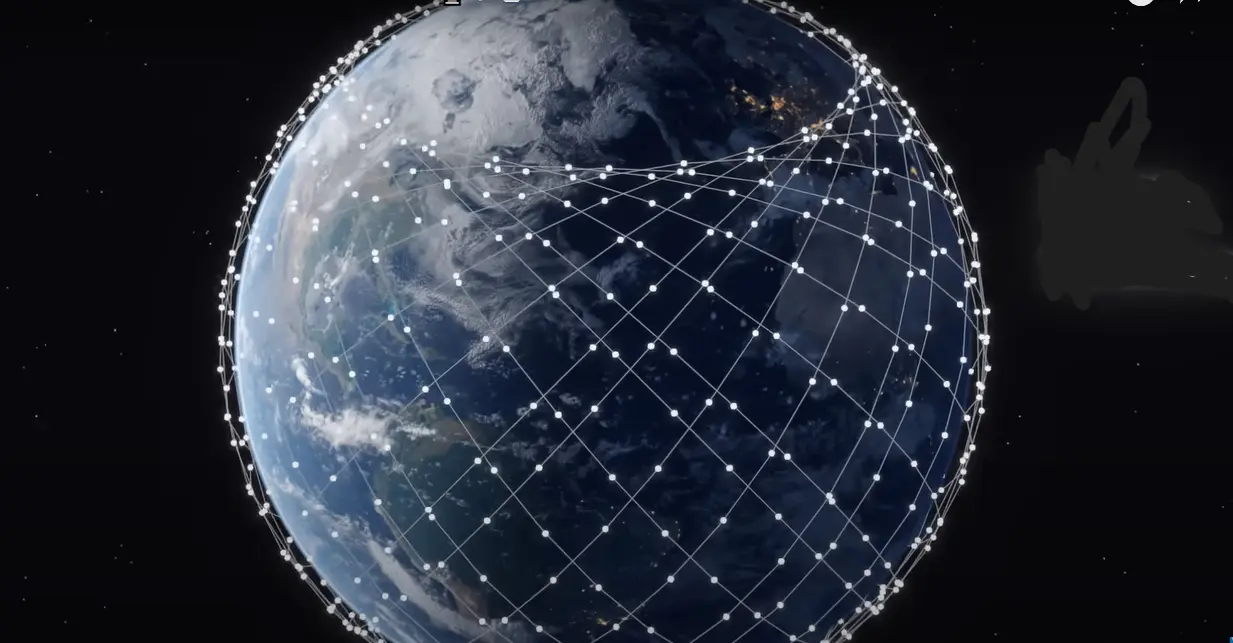
Starlink has 6,994 satellites are in orbitStars, planets, and the moon are no longer the only celestial objects visible in the night sky. These days, it also has thousands of man-made satellites, many of which are part of SpaceX’s Starlink initiative. Starlink, which aims to deliver worldwide broadband internet connectivity to even the most remote regions, has expanded quickly since its start in 2019 to become the largest satellite constellation in human history.
There are roughly 6,994 Starlink satellites in orbit as of February 2025, 6,957 of which are currently in low Earth orbit (LEO). Because SpaceX frequently launches additional satellites on its Falcon 9 rockets, this number is continuously rising.
This article will provide a thorough overview of Starlink’s ambitious project by examining its growth, technology, problems, impact, and future plans.
1. The Birth of Starlink: A Revolutionary Idea
SpaceX’s vision of a globally linked world with fast internet accessible everywhere on Earth served as the inspiration for Starlink. Due to geographic constraints, standard broadband infrastructure is either too costly or impractical to deploy in many areas.
The CEO of SpaceX, Elon Musk, had an idea for a satellite-based solution that would get beyond the drawbacks of mobile and fiber-optic networks. Starlink satellites function in low Earth orbit (~550 km or 340 miles), as opposed to conventional geostationary satellites, which orbit at 35,786 km (22,236 miles). This makes it possible for:
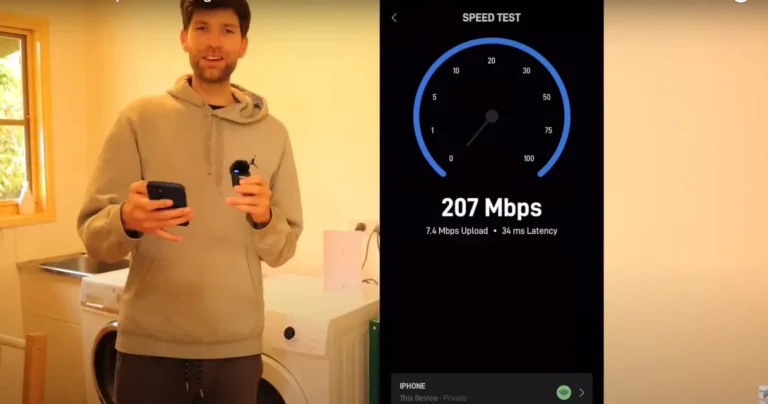
- Faster Internet Speeds (up to 1 Gbps)
- Lower Latency (as low as 25 milliseconds)
- Coverage in Remote Areas, including deserts, mountains, and oceans
Since its first operational launch in May 2019, the Starlink network has rapidly expanded, deploying thousands of satellites to build a global internet infrastructure.
2. How Many Starlink Satellites Are Currently in Orbit?
As of early 2025, Starlink’s satellite count has approached 7,000. The number of satellites in orbit is constantly increasing due to frequent launches.
Starlink’s Growth Over the Years
| Year | Satellites in Orbit | Active Satellites |
| 2019 | 60 | 60 |
| 2020 | 955 | 900 |
| 2021 | 1,740 | 1,680 |
| 2022 | 3,200 | 3,100 |
| 2023 | 4,680 | 4,500 |
| 2024 | 6,200 | 6,150 |
| 2025 | 6,994 | 6,957 |
SpaceX launches more than 50 satellites per mission, using Falcon 9 rockets for deployment. The company has plans to launch over 30,000 more satellites to improve global coverage and reliability.
3. How Starlink Satellites Work
Starlink Satellites Work each Starlink satellite weighs 260 kg (573 lbs) and is a small, solar-powered instrument. Together, they create a sizable mesh network and communicate with ground stations and one another continuously.
Essential Technology for Starlink Satellites
- Phased-Array Antennas: These antennas provide fast data transfer between ground stations and satellites.
- Optical Inter-Satellite Links (Space Lasers): Starlink satellites cut down on reliance on ground stations by communicating with one another using lasers.
- Ion Thrusters: To change their location and prevent collisions, the satellites are outfitted with ion thrusters that run on argon.
- Autonomous Collision Avoidance: Starlink satellites are able to identify and steer clear of space debris by using AI-based algorithms.
This combination of advanced technology allows Starlink to provide fast, reliable, and low-latency internet worldwide.
4. The Benefits of Starlink Internet
In terms of internet connectivity, Starlink is revolutionary, especially in underdeveloped and rural areas. The following are some of the main benefits:
- Worldwide Coverage — Operates even in far-flung locations like polar regions, islands, and deserts.
- Faster Speeds: 50 Mbps to 1 Gbps download speeds are available.
- Reduced Latency: Perfect for online work, gaming, and video calls.
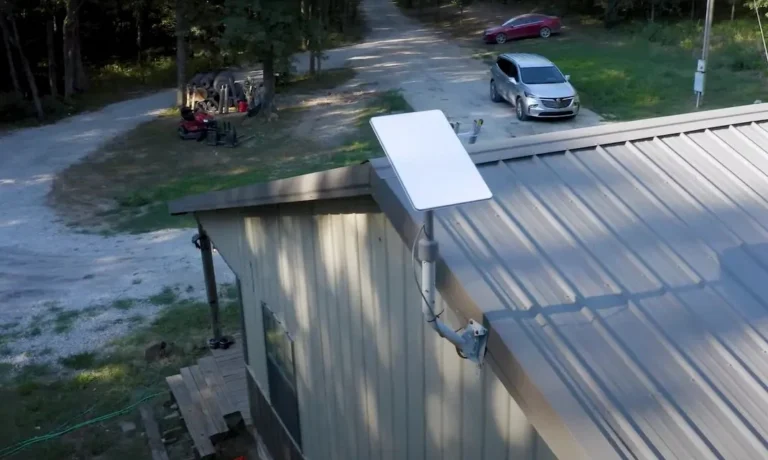
- Simple Installation: All users need is a modem and Starlink dish.
It is anticipated that nations with weak internet infrastructure—such as those in South America, Africa, and isolated regions of Asia—will gain the most from this technology.
5. Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Starlink
Starlink has been criticised and questioned despite its benefits.
A. Interference from Astronomy
Concerns over light pollution have been voiced by astronomers because Starlink satellites interfere with telescope observations by reflecting sunlight. SpaceX has responded by creating “DarkSat” coatings to lessen glare.
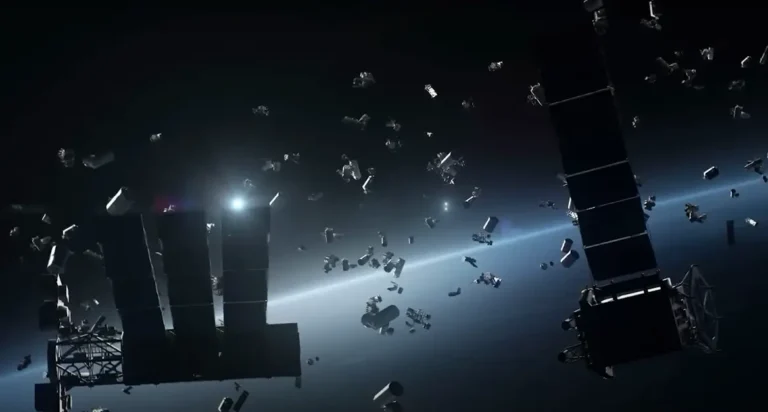
B. Risks of Collisions and Space Debris
Collisions are more likely when there are thousands of satellites in orbit. Space debris may result from a malfunctioning Starlink satellite. Although SpaceX intended for the satellites to deorbit and burn up at the end of their useful lives, there are still issues.
C. Political and Regulatory Concerns
Russia and China are among the nations that have expressed worries about Starlink’s potential use for surveillance and military objectives. Legal disputes also surround Starlink’s orbital routes and radio frequencies.
6. The Future of Starlink: What’s Next?
Among SpaceX’s ambitious goals for Starlink are the following:
- Expanding the Constellation: To improve coverage, the company aims to add 30,000+ satellites. Starlink V2.0: Bigger satellites with better power efficiency and antennae.
- Military and Government Applications – Increasing secure communications for corporations and governments.
- Starship Mega-Launches – Using the Starship rocket to launch hundreds of satellites in a single flight.
Additionally, SpaceX is working on Starlink Mini, a smaller, more affordable, and portable satellite dish.
7. How Starlink Compares to Competitors
Several companies are competing in the satellite internet space, including:
| Company | Project Name | Satellites Planned | Status |
| SpaceX | Starlink | 30,000+ | Operational |
| Amazon | Project Kuiper | 3,236 | Launching 2025 |
| OneWeb | OneWeb | 648 | Operational |
| China | Guowang | 13,000 | In Development |
Starlink remains the dominant player, but competition is expected to increase in the coming years.
8. Is Starlink the Future of Internet Connectivity?
In remote locations, satellite internet may eventually take the role of regular broadband as the world grows increasingly digitally linked. Starlink is a viable option for global connectivity because of its capacity to provide high-speed, low-latency internet everywhere.
However, issues like cost, restrictions, and space congestion may ultimately determine Starlink’s level of success.
Conclusion
Starlink is changing the internet landscape with 6,994 satellites in space and additional planned launches. SpaceX is crossing the digital divide like never before by providing high-speed, low-latency internet all over the world.
Starlink is still at the forefront of satellite broadband technology in spite of issues with regulations, astronomical interference, and space debris. The future of space-based internet is expected to be inventive, competitive, and revolutionary as additional rivals join the market.